COMPUTER DEFINITION A computer is a machine or device that performs processes, calculations and operations based on instructions provided by a software or hardware program. It is designed to execute applications and provides a variety of solutions by combining integrated hardware and software components.
A computer is a machine or device that performs processes, calculations and operations based on instructions provided by a software or hardware program. It is designed to execute applications and provides a variety of solutions by combining integrated hardware and software components.
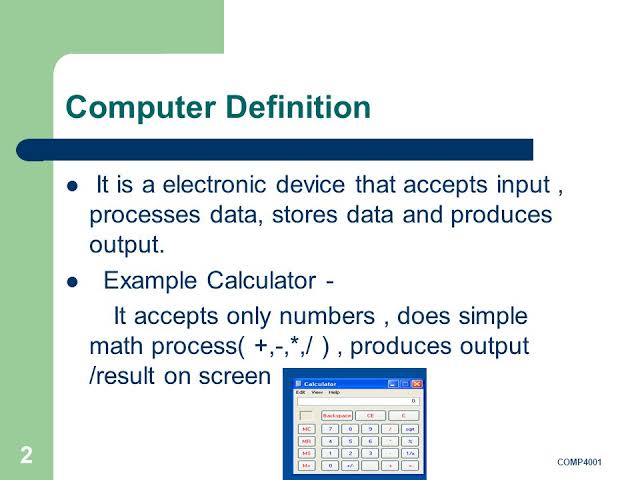
Computer is derived from a Latin word “computare” which means to “to calculate”, “to count”, “to sum up” or“to think together”. So, more precisely the word computer means a “device that performs computation“.
The computer is also called an organizer or PC. PC comes from the English name “Personal Computer”.
There are also portable computers known as “laptop”, that are easy to carry from one place to another
because of their smaller size.
Generally, all computers have the same basic computer parts such as: monitor, keyboard, mouse, USB
unit, CD ROM unit, CPU (Central Processing Unit).
A device, usually electronic, that. processes data according to a set ofinstructions. The digital computer storesdata in discrete units and performsarithmetical and logical operations atvery high speed. The analog computerhas no memory and is slower than thedigital computer but has a continuousrather than a discrete input. The hybridcomputer combines some of theadvantages of digital and analogcomputersSee also digital computer,analog computer, hybrid computer
A programmable machine that performshigh-speed processing of numbers, as wellas of text, graphics, symbols, and sound.All computers contain a central processingunit that interprets and executesinstructions; input devices, such as akeyboard and a mouse, through which dataand commands enter the computer;memory that enables the computer to storeprograms and data; and output devices,such as printers and display screens, thatshow the results after the computer hasprocessed data.
COMPUTER FUNCTION
The four functions of a computer actually explain the core reasons why it was built. They include:
- Data input
- Data processing.
- Information output.
- Data and information storage.

For example, the user composes a letter by inputting and editing sets of letters, numbers and symbols using a keyboard. The raw data is then processed and viewed real-time via display hardware.
The user may choose to print the letter onto paper, or better still send it via electronic mail to intended recipients.
The same data and information can be retained digitally in disk drives and other media for future reference.
1. Data Input
Every computer is designed with data input as a first function, an activity which is accomplished via input devices.
Data entry is done manually, automatically or both. Manual input is done via add-on peripherals like the keyboard, mouse and stylus. Input can also be accomplished via vocal dictation applications and body gestures peripherals like Kinect and biometric devices. Elsewhere, data input is also done using secondary storage media and networking interfaces.
Application software used for this purpose will also dictate what data is entered. Word processing software is designed to input basic alphanumerical data, while a photo editing application is used to input and manipulate images.
This data may be entered into a database, spreadsheet or other forms of a computerized work area.
Automated applications and robotics can also be used to intelligently feed data into the computer on station or remotely. As an example, tallying of electoral process can be accomplished remotely and automatically.
Nowadays, computers come in all shapes and sizes. From mini-computers to supercomputers and servers, there are options available to suit everyone’s taste and budget. The latest models boast VR technology, 5G connectivity, 4K screens and other advanced features. However, not everyone needs these extras.
The computer operates according to instructions stored in its own memory unit and can accept inputted data, process that data arithmetically; and through sequence-based logic, it can produce information and store the results for future use. All the applications of a computer derive from one of these four functions.
The computer operates according to instructions stored in its own memory unit and can accept inputted data, process that data arithmetically; and through sequence-based logic, it can produce information and store the results for future use. All the applications of a computer derive from one of these four functions.

Laptop Keyboard and touchpad
2. Data Processing
Data processing is the core function of a computer. Processing involves manipulation of raw data into before converting it into meaningful information. Usually, data is in raw form, and will thus undergo processing before dissemination for user consumption.
The ‘brain’ of the computer where data is processed is referred to as the microprocessor. It is also commonly known as the central processing unit (CPU) or accelerated processing unit (APU).
The processing chips in modern personal computing devices continue to evolve and outperform its predecessors. One particular evolution is the merger of microprocessor and graphics processing unit (GPU) into what is now known as accelerated processing unit. The merger allows for the integration of powerful graphics processing abilities inside the traditional arithmetic and logical computations of the processor.
Besides the microprocessor, the dynamic random access memory (DRAM) and static random access memory (SRAM) are integral parts of data processing. Data entered via input devices is stored temporarily in DRAM, then transferred to SRAM from where the microprocessor manipulates it.
 An AMD microprocessor, inserted onto a laptop motherboard socket
An AMD microprocessor, inserted onto a laptop motherboard socket3. Information Output
When raw data has been manipulated by the microprocessor, the outcome is meant to be disseminated for useful purposes. The output is thus referred to as information and is beneficial to the computer user.
Processed data or information can be,
- viewed as alphanumeric, images and video via a display hardware
- listened to as audio files by use of a speaker
- printed as hard copy output onto paper
- printed as 3D models

4. Data and Information Storage
The fourth and equally very important function of a computer is data and information storage. After sleepless nights of video and animation creation and editing, the user wants to have the finished product stored for future dissemination and additional editing.
A computer can store information internally and externally. The hard disk drive (HDD) and/or solid-state disk drive (SSD) are internal storage devices and serve to protect and house all data and information on a computer. In bigger systems, the RAID system is used. Multiple disk drives operate simultaneously to ensure data and information integrity.
External storage is achieved through accessories that attach externally to the computer. They include external drives and optical disks.
Better still data and information can be stored online in cloud solutions for a fee or for a fee if large space is required.
Storage integrity is a crucial phase that can actually determine the worth of a computer system. In any case, what use is a computer without data and information?

References:
1. https://www.techopedia.com/definition/4607/computer
2. http://www.byte-notes.com/what-computer
5.https://www.enotes.com/homework-help/what-functions-computer-91081
6. https://bizfluent.com/list-5900482-five-basic-functions-computer-system.html













