“The purpose of technology is not to confuse the brain but to serve the body.”
– William S. Burroughs
Technology is a collection of skills, technique, and methods. A science or knowledge put into practical use to solve problems or invent useful tools. It serves convenience to every living things.
Computer is one of the symbol of technology. But, where did it came from? Who invented this?
1837 – Analytical Engine
The Analytical Engine was a proposed mechanical general-purpose computer designed by English mathematician and computer pioneer Charles Babbage. It was first described in1837 as the successor to Babbage’s difference engine, a design for a mechanical computer.  Analytical Engine by Charles Babbage
Analytical Engine by Charles Babbage
1936 – Z1
A man named Konrad Zuse, a german engineer, invented the world’s first programmable computer, the “Z1” . It was an electrically driven mechanical calculator with limited programmability, reading instructions from punched celluloid film. Unfortunately, Z1 was destroyed during WWII. But, he came back in 1941 to finish the “Z3“. It was used for aerodynamic calculations but was destroyed in a bombing raid on Berlin in late 1943. Zuse later supervised a reconstruction of the Z3 in the 1960s, which is currently on display at the Deutsches Museum in Munich.
 Konrad Zuse
Konrad Zuse
1939 – HP
An American multinational information technology company headquartered in Palo Alto, California. It is the Hewlett-Packard. It is founded by David Packard and Bill Hewlett in their own garage. HP 200A Audio Oscillator is their first product, rapidly became a popular piece of test equipment for engineers.  Bill Hewlett and David Packard
Bill Hewlett and David Packard
1948 – Manchester Baby
University of Manchester researchers Frederic Williams, Tom Kilburn, and Geoff Toothill developed the Small-Scale Experimental Machine (SSEM), better known as the Manchester “Baby.” It was built to test a new memory technology developed by Williams and Kilburn — soon known as the Williams Tube – which was the first electronic random access memory for computers. The first program, consisting of seventeen instructions and written by Kilburn, ran on June 21st, 1948. This was the first program to ever run on an electronic stored-program computer.  Frederic Williams and Tom Kilburn
Frederic Williams and Tom Kilburn
1948 – ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator And Computer)
The world’s first general-purpose computer was created, the ENIAC computing system that was built by John Mauchly and J. Presper Eckert at the Moore School of Electrical Engineering of the University of Pennsylvania. It is over 1,000 times faster than any previous computer. ENIAC used panel-to-panel wiring and switches for programming, occupied more than 1,000 square feet, used about 18,000 vacuum tubes and weighed 30 tons. It was believed that ENIAC had done more calculation over the ten years it was in operation than all of humanity had until that time. ENIAC
1951 – First UNIVAC
The Univac 1 is the first commercial computer to attract widespread public attention. Although manufactured by Remington Rand, the machine was often mistakenly referred to as “the IBM Univac.” Univac computers were used in many different applications but utilities, insurance companies and the US military were major customers. One biblical scholar even used a Univac 1 to compile a concordance to the King James version of the Bible. Created by Presper Eckert and John Mauchly — designers of the earlier ENIAC computer — the Univac 1 used 5,200 vacuum tubes and weighed 29,000 pounds. Remington Rand eventually sold 46 Univac 1s at more than $1 million each.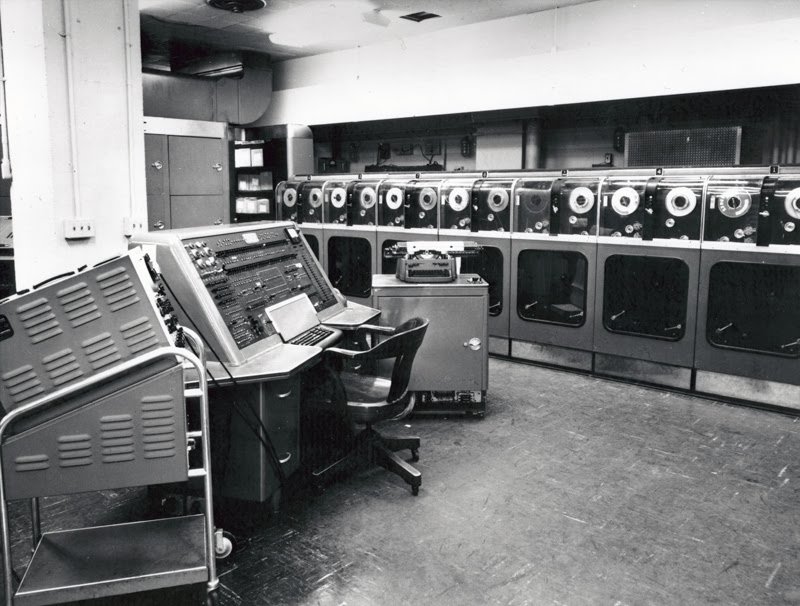  UNIVAC
UNIVAC
1952 – IAS Computer
The IAS machine was the first electronic computer to be built at the Institute for Advanced Study (IAS) in Princeton, New Jersey. It is sometimes called the von Neumann machine, since the paper describing its design was edited by John von Neumann, a mathematics professor at both Princeton University and IAS. IAS Computer
1961 – NEAC 2203
The NEAC (Nippon Electric Automatic Computer) includes a CPU, console, paper tape reader and punch, printer and magnetic tape units. It was exclusively sold in Japan, and it could process alphabetic and Japanese kana characters. NEAC 2203
1964 – CDC 6600
The CDC 6600 was the flagship of the 6000 series of mainframe computer systems manufactured by Control Data Corporation. Generally considered to be the first successful supercomputer, it outperformed the industry’s prior recordholder, the IBM 7030 Stretch, by a factor of three.  CDC 6600 supercomputer
CDC 6600 supercomputer
1971 – Intel’s first microprocessor
The Intel 4004 is a 4-bit central processing unit released by Intel Corporation in 1971. It was the first commercially available microprocessor by Intel, and the first in a long line of Intel CPUs. Developed for Busicom, a Japanese calculator maker, the 4004 had 2250 transistors and could perform up to 90,000 operations per second in four-bit chunks.  Intel 4004
Intel 4004
1976 – Apple-1
Designed by Steve Wozniak from Sunnyvale, California and marketed by his friend, Steve Jobs, the Apple-1 is a single-board computer for enthusiasts. With an order for 50 assembled systems from Mountain View, California computer store The Byte Shop in hand, the duo started a new company, naming it Apple Computer, Inc. In all, about 200 of the boards were sold before Apple announced the follow-on Apple II a year later as a ready-to-use computer for consumers, a model which sold in the millions for almost twenty years./https%3A%2F%2Fblueprint-api-production.s3.amazonaws.com%2Fuploads%2Fcard%2Fimage%2F513198%2F507d2e33-22d3-4032-9273-22d87feecdfc.jpg) Apple-1
Apple-1
1982 – IBM PC (Personal Computers)
The IBM Personal Computer, commonly known as the IBM PC, is the original version and progenitor of the IBM PC compatible hardware platform. The IBM PC revolutionized business computing by becoming the first PC to gain widespread adoption by industry. The IBM PC was widely copied (“cloned”) and led to the creation of a vast “ecosystem” of software, peripherals, and other commodities for use with the platform.  IBM PC
IBM PC
1984 – Apple introduces Macintosh
The Macintosh was the first successful mouse-driven computer with a graphical user interface and was based on the Motorola 68000 microprocessor. Its price was $2,500. Applications that came as part of the package included MacPaint, which made use of the mouse, and MacWrite, which demonstrated WYSIWYG (What You See Is What You Get) word processing.  Macintosh
Macintosh
1988 – NeXT Cube
The NeXT had three Motorola microprocessors and 8 MB of RAM. Its base price was $6,500. Some of its other innovations were the inclusion of a magneto-optical (MO) disk drive, a digital signal processor and the NeXTSTEP programming environment (later released as OPENSTEP). This object-oriented multitasking operating system was groundbreaking in its ability to foster rapid development of software applications. OPENSTEP was used as one of the foundations for the new Mac OS operating system soon after NeXT was acquired by Apple in 1996.  NeXT Cube
NeXT Cube
1996 – Palm Pilot
The first generation of Palm-produced devices, the Palm 1000 and 5000, are based around a Motorola microprocessor running at 16MHz, and uses a special gestural input language called “Graffiti,” which is quick to learn and fast. Palm could be connected to a PC or Mac using a serial port to synchronize – “sync” – both computer and Palm. The company called it a ‘connected organizer’ rather than a PDA to emphasize this ability.  Palm Pilot
Palm Pilot
1996 – Sony Vaio
Sony had manufactured and sold computers in Japan, but the VAIO signals their entry into the global computer market. The first VAIO, a desktop computer, featured an additional 3D interface on top of the Windows 95 operating system as a way of attracting new users. The VAIO line of computers would be best known for laptops were designed with communications and audio-video capabilities at the forefront, including innovative designs that incorporated TV and radio tuners, web cameras, and handwriting recognition. The line was discontinued in 2014.  Sony Vaio Laptop
Sony Vaio Laptop
2000 – First Camera Phone
Japan’s SoftBank introduces the first camera phone, the J-Phone J-SH04; a Sharp-manufactured digital phone with integrated camera. The camera had a maximum resolution of 0.11 megapixels a 256-color display, and photos could be shared wirelessly. The J-Phone line would quickly expand, releasing a flip-phone version just a month later. Cameras would become a significant part of most phones within a year, and several countries have even passed laws regulating their use.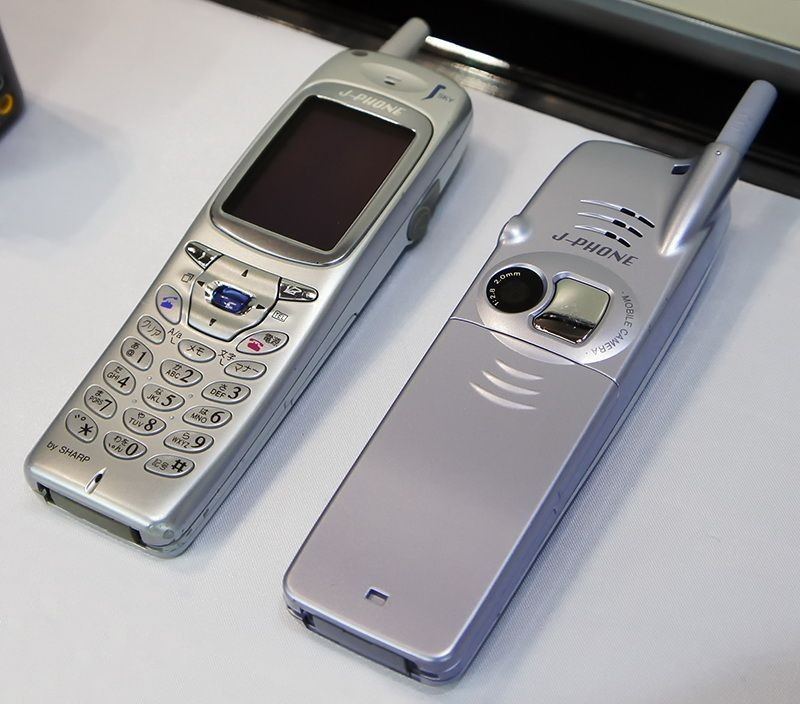  First Camera Phone
First Camera Phone
2007 – Amazon Kindle
Many companies have attempted to release electronic reading systems dating back to the early 1990s. Online retailer Amazon released the Kindle, one of the first to gain a large following among consumers. The first Kindle featured wireless access to content via Amazon.com, along with an SD card slot allowing increased storage. The first release proved so popular there was a long delay in delivering systems on release. Follow-on versions of the Kindle added further audio-video capabilities.  Amazon Kindle
Amazon Kindle
2007 – Apple iPhone
Apple launches the iPhone – a combination of web browser, music player and cell phone – which could download new functionality in the form of “apps” (applications) from the online Apple store. The touchscreen enabled smartphone also had built-in GPS navigation, high-definition camera, texting, calendar, voice dictation, and weather reports.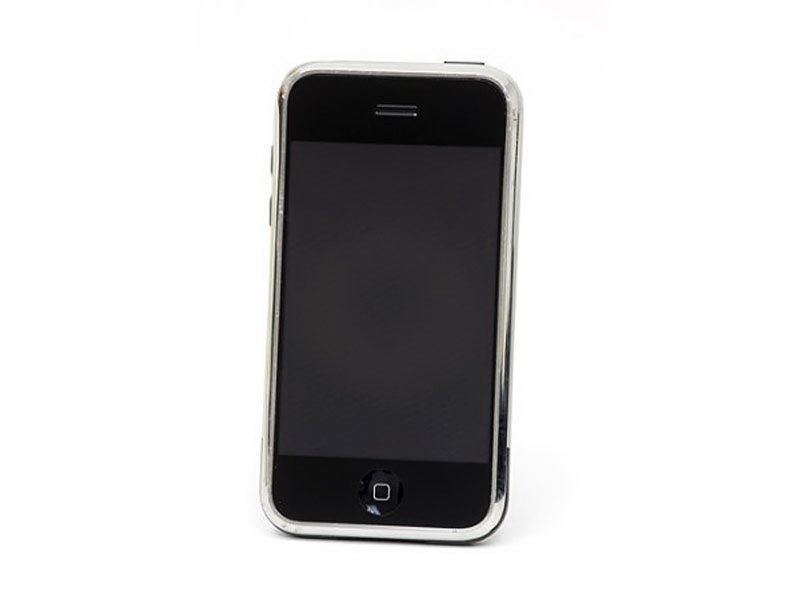  iPhone
iPhone
2008 – Macbook Air
Apple introduces their first ultra notebook – a light, thin laptop with high-capacity battery. The Air incorporated many of the technologies that had been associated with Apple’s MacBook line of laptops, including integrated camera, and Wi-Fi capabilities. To reduce its size, the traditional hard drive was replaced with a solid-state disk, the first mass-market computer to do so.  Macbook Air and Steve Jobs
Macbook Air and Steve Jobs
2011 – iPad
The iPad combines many of the popular capabilities of the iPhone, such as built-in high-definition camera, access to the iTunes Store, and audio-video capabilities, but with a nine-inch screen and without the phone. Apps, games, and accessories helped spur the popularity of the iPad and led to its adoption in thousands of different applications from movie making, creating art, making music, inventory control and point-of-sale systems, to name but a few.  iPad
iPad
2015 – Apple Watch
Building a computer into the watch form factor has been attempted many times but the release of the Apple Watch leads to a new level of excitement. Incorporating a version of Apple’s iOS operating system, as well as sensors for environmental and health monitoring, the Apple Watch was designed to be incorporated into the Apple environment with compatibility with iPhones and Mac Books. Almost a million units were ordered on the day of release. The Watch was received with great enthusiasm, but critics took issue with the somewhat limited battery life and high price.  Apple Watch
Apple Watch
References :
Analytical Engine – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Analytical_Engine Z1 – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Z1_(computer) HP- http://www.computerhistory.org/timeline/computers/#169ebbe2ad45559efbc6eb35720ca6db Manchester Baby – http://www.computerhistory.org/timeline/computers/#169ebbe2ad45559efbc6eb3572083fb7 ENIAC – http://www.computerhistory.org/timeline/computers/#169ebbe2ad45559efbc6eb3572043c44 The UNIVAC – http://www.computerhistory.org/timeline/computers/#169ebbe2ad45559efbc6eb35720347da IAS- http://www.computerhistory.org/timeline/computers/#169ebbe2ad45559efbc6eb3572069066 NEAC 2203 – http://www.computerhistory.org/timeline/computers/#169ebbe2ad45559efbc6eb3572012c35 CDC 6600 – http://www.computerhistory.org/timeline/computers/#169ebbe2ad45559efbc6eb3572081363 Intel’s First Microprocessor – http://www.computerhistory.org/timeline/computers/#169ebbe2ad45559efbc6eb35720a911b Apple 1 – http://www.computerhistory.org/timeline/computers/#169ebbe2ad45559efbc6eb35720c0788 IBM PC – http://www.computerhistory.org/timeline/computers/#169ebbe2ad45559efbc6eb35720105c3 Macintosh – http://www.computerhistory.org/timeline/1984/#169ebbe2ad45559efbc6eb3572026cc9 NeXT Cube – http://www.computerhistory.org/timeline/1988/#169ebbe2ad45559efbc6eb357201007e Palm Pilot – http://www.computerhistory.org/timeline/computers/#169ebbe2ad45559efbc6eb35720753f8 Sony Vaio – http://www.computerhistory.org/timeline/computers/#169ebbe2ad45559efbc6eb35720aa02c First Camera Phone – http://www.computerhistory.org/timeline/computers/#169ebbe2ad45559efbc6eb35720c644b Amazon Kindle – http://www.computerhistory.org/timeline/computers/#169ebbe2ad45559efbc6eb357203cff2 iPhone – http://www.computerhistory.org/timeline/computers/#169ebbe2ad45559efbc6eb357201368b Macbook Air – http://www.computerhistory.org/timeline/computers/#169ebbe2ad45559efbc6eb357203a8a7 Apple Ipad – http://www.computerhistory.org/timeline/computers/#169ebbe2ad45559efbc6eb35720325d4 Apple Watch – http://www.computerhistory.org/timeline/computers/#169ebbe2ad45559efbc6eb357208f34c
 A computer is a machine or device that performs processes, calculations and operations based on instructions provided by a software or hardware program. It is designed to execute applications and provides a variety of solutions by combining integrated hardware and software components.
A computer is a machine or device that performs processes, calculations and operations based on instructions provided by a software or hardware program. It is designed to execute applications and provides a variety of solutions by combining integrated hardware and software components.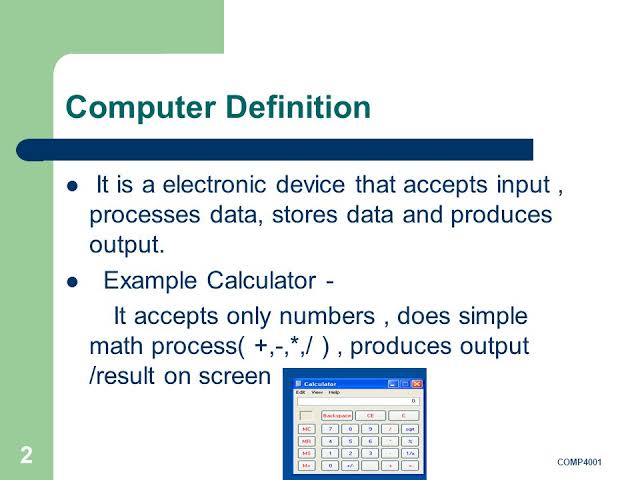


 An AMD microprocessor, inserted onto a laptop motherboard socket
An AMD microprocessor, inserted onto a laptop motherboard socket




















































